Lens

लेंस आमतौर पर कांच या पारदर्शी प्लास्टिक का बनाया जाता है।
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.lens a transparent optical device used to converge or diverge transmitted light and to form images
ताल(lens) को मुख्य रूप से दो वर्गों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है,
- उत्तल ताल (convex lens)
ये लैंस बीच में मोटे तथा किनारों पर पतले होते हैं । ये आपतित प्रकाश किरणों को एक बिन्दु पर एकत्रित करते हैं ।
- अवतल ताल (concave lens)
ये लैंस किनारों पर मोटे तथा बीच में पतले होते हैं । ये लैंस आपतित प्रकाश किरणों को फैला देते हैं ।
ताल के उपयोग
- प्रकाशीय यंत्रों (कैमरा, दूरदर्शी, सूक्ष्मदर्शी आदि) में
- आँख के चश्मों में
- प्रकाश को अभिकेन्द्रित करने के लिये
Difference Between Convex and Concave Lens
The lens is understood as a curved and transparent piece of glass or plastic, which focuses and refracts light rays in a certain manner. The curvature of the object ascertains the extent to which light is bent and in which direction. They are used in spectacles, microscope and telescopes. Based on the shape, the lens can be grouped as a convex lens or concave lens. The former brings together the parallel beam of light, while the latter disperses it.
So, the point of focus in case of the convex lens is the point where all the light rays meet, i.e. point of convergence, but if we talk about the concave lens, the focal point is the point from where the light rays seem to diverge, i.e. point of divergence.
Definition of Convex Lens
Convex Lenses are the lenses that feel massive at the centre than at the edges. The curve of the lens is outward, and as the light beams pass through the lens, it refracts them and brings them together, resulting in the convergence of light, due to which it is also named as a converging lens. Look at the figure given below:
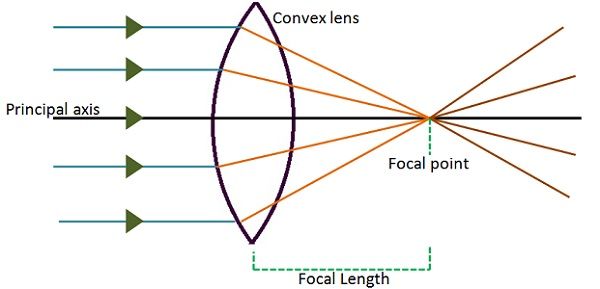
So, the point where the light rays meet is known as a focal point, or principal focus and space amidst the centre of the lens and the principal focus is the focal length. Further, it generates a real and inverted image, but it can also form a virtual image when the object is placed too close to the lens. Such lenses are used to focus a beam of light on making the object look clearer and larger.
Example: The lenses of a camera are a convex lens, as the light rays focus on person or object being captured.
Definition of Concave Lens
Concave lenses represent the type of lenses which are slender at the centre than at the borders. The shape of a concave lense is round inward that bends the beams outward, causing divergence of the rays of light falling on it, so it is known as a diverging lens. This also makes the object look smaller and farther than they really are and the image formed is virtual, diminished and upright.
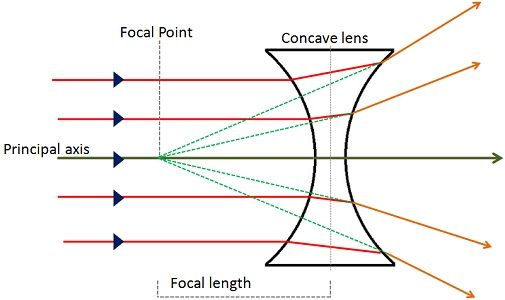
As you can see in the given figure, the light rays appear to be diverging from a virtual point, which is known as principal focus or focal point. Further, the length between the focal point and the centre of the lens is called focal length.
Example: Concave lenses are used in the side mirrors of cars and motorbikes. They can also be used in movie projectors to spread the image.
Comparison Chart
1. अवतल दर्पण में, किसी वस्तु की छवि:
A. जब वस्तु वक्रता के केंद्र से बाहर होती है तो छवि वास्तविक, सीधी और छोटी बनती है.
B. जब वस्तु वक्रता और फ़ोकस के केंद्र के बीच होती है तो छवि वास्तविक, उल्टी और समान आकार की बनती है.
C. जब वस्तु वक्रता के केंद्र से परे होती है तो छवि वास्तविक, उल्टी और छोटी बनती है.
D. वास्तविक, बड़ी और अप्रतिबंधिक नहीं होती है.
Ans. c
2. एक दूरबीन की आवर्धक शक्ति को बढ़ाने के लिए, फोकल लम्बाई:
A. उद्देश्य लेंस की बढ़ाई जानी चाहिए.
B. उद्देश्य लेंस की कम होनी चाहिए.
C. आई-पीस लेंस को बढ़ाया जाना चाहिए.
D. आई-पीस लेंस को घटाना चाहिए.
Ans. d
3. सागर नीला क्यों दिखता है?
A. क्योंकि सूर्य की रोशनी जब पढ़ती है तो प्रतिबिंबित होती है.
B. क्योंकि सूर्य की रोशनी जब पढ़ती है तो अपवर्तित होती है.
C. क्योंकि सूर्य का प्रकाश जब गिरता है तो अवशोषित हो जाता है.
D. क्योंकि सूर्य का प्रकाश उस पर गिरने से बिखर जाता है.
Ans. d
4. अवतल लेंस की पॉवर क्या है?
A. पॉजिटिव
B. नेगेटिव
C. उपरोक्त दोनों
D. उपरोक्त दोनों में से कोई नहीं
Ans. b
5. कौन सा चश्मा या लेंस का उपयोग निकट दृष्टि दोषों को ठीक करने के लिए किया जाता है?
A. अवतल लेंस
B. उत्तल लेंस
C. द्विध्रुवी लेंस
D. उपरोक्त में से कोई नहीं
Ans. a
A. जब वस्तु वक्रता के केंद्र से बाहर होती है तो छवि वास्तविक, सीधी और छोटी बनती है.
B. जब वस्तु वक्रता और फ़ोकस के केंद्र के बीच होती है तो छवि वास्तविक, उल्टी और समान आकार की बनती है.
C. जब वस्तु वक्रता के केंद्र से परे होती है तो छवि वास्तविक, उल्टी और छोटी बनती है.
D. वास्तविक, बड़ी और अप्रतिबंधिक नहीं होती है.
Ans. c
2. एक दूरबीन की आवर्धक शक्ति को बढ़ाने के लिए, फोकल लम्बाई:
A. उद्देश्य लेंस की बढ़ाई जानी चाहिए.
B. उद्देश्य लेंस की कम होनी चाहिए.
C. आई-पीस लेंस को बढ़ाया जाना चाहिए.
D. आई-पीस लेंस को घटाना चाहिए.
Ans. d
3. सागर नीला क्यों दिखता है?
A. क्योंकि सूर्य की रोशनी जब पढ़ती है तो प्रतिबिंबित होती है.
B. क्योंकि सूर्य की रोशनी जब पढ़ती है तो अपवर्तित होती है.
C. क्योंकि सूर्य का प्रकाश जब गिरता है तो अवशोषित हो जाता है.
D. क्योंकि सूर्य का प्रकाश उस पर गिरने से बिखर जाता है.
Ans. d
4. अवतल लेंस की पॉवर क्या है?
A. पॉजिटिव
B. नेगेटिव
C. उपरोक्त दोनों
D. उपरोक्त दोनों में से कोई नहीं
Ans. b
5. कौन सा चश्मा या लेंस का उपयोग निकट दृष्टि दोषों को ठीक करने के लिए किया जाता है?
A. अवतल लेंस
B. उत्तल लेंस
C. द्विध्रुवी लेंस
D. उपरोक्त में से कोई नहीं
Ans. a
6. प्रोजेक्टर में किस लेंस का इस्तेमाल होता है?
A. उत्तल लेंस
B. अवतल लेंस
C. द्विध्रुवी लेंस
D. दोनों A और B
Ans. a
7. किस घटना के कारण पानी में डूबी हुई छड़ी ऊपर उठी हुई दिखाई देती है?
A. परावर्तन
B. प्रकीर्णन
C. अपवर्तन
D. विक्षेपण
Ans. c
8. किस घटना के कारण जब सिनेमा मशीन से किरणें निकलती हैं तो वह स्क्रीन पर उबरती हुई क्यों दिखती हैं?
A. प्रकीर्णन
B.विवर्तन
C. विक्षेपण
D. अपवर्तन
Ans. b
9. दांतों का दर्पण किस प्रकार का दर्पण है?
A. उत्तल दर्पण
B. अवतल दर्पण
C. प्लेन दर्पण
D. दोनों B और C
Ans. d
10. दुकान-उठाने वाले उपकरणों में किस तरह के दर्पण का उपयोग किया जाता है?
A. अवतल दर्पण
B. उत्तल दर्पण
C. प्लेन दर्पण
D. उपरोक्त में से कोई नहीं
Ans. b
A. उत्तल लेंस
B. अवतल लेंस
C. द्विध्रुवी लेंस
D. दोनों A और B
Ans. a
7. किस घटना के कारण पानी में डूबी हुई छड़ी ऊपर उठी हुई दिखाई देती है?
A. परावर्तन
B. प्रकीर्णन
C. अपवर्तन
D. विक्षेपण
Ans. c
8. किस घटना के कारण जब सिनेमा मशीन से किरणें निकलती हैं तो वह स्क्रीन पर उबरती हुई क्यों दिखती हैं?
A. प्रकीर्णन
B.विवर्तन
C. विक्षेपण
D. अपवर्तन
Ans. b
9. दांतों का दर्पण किस प्रकार का दर्पण है?
A. उत्तल दर्पण
B. अवतल दर्पण
C. प्लेन दर्पण
D. दोनों B और C
Ans. d
10. दुकान-उठाने वाले उपकरणों में किस तरह के दर्पण का उपयोग किया जाता है?
A. अवतल दर्पण
B. उत्तल दर्पण
C. प्लेन दर्पण
D. उपरोक्त में से कोई नहीं
Ans. b






Comments
Post a Comment